Lipoproteins, Apolipoproteins Metabolism and transport , Fatty acid biosynthesis (Lipogenesis)
Vložit
- čas přidán 16. 11. 2023
- 📌 𝐅𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐨𝐧 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦:- / drgbhanuprakash
📌𝗝𝗼𝗶𝗻 𝗢𝘂𝗿 𝗧𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗺 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗻𝗲𝗹 𝗛𝗲𝗿𝗲:- t.me/bhanuprakashdr
📌𝗦𝘂𝗯𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗯𝗲 𝗧𝗼 𝗠𝘆 𝗠𝗮𝗶𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗟𝗶𝘀𝘁:- linktr.ee/DrGBhanuprakash
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins Metabolism:
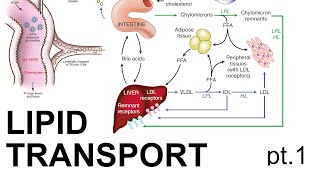
Lipoproteins Overview: Lipoproteins are complex molecular structures composed of lipids and proteins. They play a crucial role in lipid transport and metabolism in the body. Understanding their metabolism is fundamental to comprehending cholesterol and triglyceride regulation.
Types of Lipoproteins:
______________________
1. Chylomicrons: These are large lipoproteins formed in the intestinal mucosa to transport dietary triglycerides to various tissues.
2. Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL): Synthesized in the liver, they transport endogenous triglycerides to tissues.
3. Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL): Formed from VLDL metabolism, they carry cholesterol to cells and are known as "bad cholesterol."
4. High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL): Produced in the liver and small intestine, they transport excess cholesterol from tissues to the liver for excretion and are considered "good cholesterol."
Apolipoproteins Function: Apolipoproteins are proteins associated with lipoproteins and serve various functions, including lipid solubilization, enzyme co-factors, and receptor recognition.
Metabolism:
____________
1. Chylomicron Metabolism: Chylomicrons are synthesized in the intestine and transport dietary triglycerides to various tissues. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) on capillary endothelial cells hydrolyzes their triglycerides, allowing tissues to take up fatty acids for energy or storage.
2. VLDL Metabolism: The liver synthesizes VLDL to transport endogenous triglycerides. As VLDL circulates, triglycerides are hydrolyzed by LPL, converting VLDL to IDL (Intermediate Density Lipoprotein) and then to LDL. LDL delivers cholesterol to cells via LDL receptors.
3. HDL Metabolism: HDL particles pick up excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues and transport it to the liver in a process called reverse cholesterol transport.
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis (Lipogenesis):
_____________________________________
Overview: Fatty acid biosynthesis, also known as lipogenesis, is the process by which cells synthesize fatty acids from acetyl-CoA. This is an anabolic pathway primarily occurring in the liver and adipose tissue.
Steps of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis:
1. Acetyl-CoA Carboxylation: Acetyl-CoA is carboxylated to form malonyl-CoA, a crucial precursor.
2. Fatty Acid Synthesis: Repeated condensation of malonyl-CoA with acetyl-CoA by fatty acid synthase (FAS) produces long-chain fatty acids.
3. Elongation and Desaturation: Further modification can occur to elongate or introduce double bonds into the fatty acid chain.
4. Formation of Triglycerides: Fatty acids are esterified to glycerol to form triglycerides, which are stored in adipose tissue or transported as lipoproteins.
Regulation: Fatty acid biosynthesis is tightly regulated by insulin, which promotes lipogenesis by activating key enzymes and inhibiting fatty acid breakdown. Conversely, glucagon and adrenaline inhibit lipogenesis during fasting or stress.
#fmge #fmgevideos #rapidrevisionfmge #fmgejan2023 #mbbslectures #nationalexitexam #nationalexittest #neetpg #usmlepreparation #usmlestep1 #fmge #usmle #drgbhanuprakash #medicalstudents #medicalstudent #medicalcollege #neetpg2023 #usmleprep #usmlevideos #usmlestep1videos #medicalstudents #neetpgvideos #usmlebiochemistry #biochemistry #lipogenesis #biochemistryvideos








Thnkyu
Good
❤❤