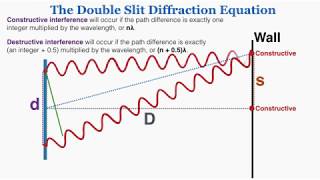
Deriving Young’s Double Slit Interference Formulas
Vložit
- čas přidán 27. 02. 2021
- In this video, I derive two different, but related, versions of Young’s double slit interference equations. These equations are used to find the points of constructive interference on a screen a distance D away.








the only video that explained why the angle is concidered 90 degrees. I didn't understand it watching so many other explainations. Good job!
Excellent video. I also teach physics, in Pakistan. I was unable to find a way how to explain theta = theta to my students, so here it is a great video.
This video is so thoroughly explained, but in a way that is easy to comprehend. Not to mention the approximations which few sources seem to acknlowedge.
Thanks so much.
Thanks for watching and yeah that was the real impetus for making this one, I really didn’t get this formula until I got the approximations and then it’s kinda trivial
@@TheBrainFillerThanks a lot man, I was looking for this exact same thing too
Finally someone covered the angle theta which is introduced in the books out of nowhere. It is useful to that we take central maximum as our reference point.
Holy shit….dude this video is so underrated and best one I’ve ever saw……thank you so much for this
Thanks so much! That’s great to hear
Thanks for this video. I appreciate your acknowledgement of the assumptions used here, specifically that the 3 lines are assumed to be parallel. My textbook completely glossed over this fact and skipped to the diagram which had me questioning myself since the geometry didn't line up :)
No problem thanks for watching
Thank you so much for clarifying that the lines being parallell is an approximation. I kept finding that they had to be parallell when trying to derive this, which confused the hell out of me. Neither my teacher nor my book mentioned it.
Yeah wrapping my head around that was the toughest part for me too
Thank you for the simple and informative explanation.
Thanks for watching
fantastic video. Really concise clear and t the point. thank you
Thanks for explaining the assumptions which made it all clear.
Great video!
really good for concept building...appreciate the work
Awesome thanks for watching…that’s definitely my goal
Great explanation , thank you so much
This is such a good guide
Thank you so much bro, I only understood from you for this topic
Best explanation......thank you👍👍
thanks for the videoand for clarifying that the lines being parallell is an approximation, this point made me so confused until i didnt watch the video
thanks man, it really helped
Was extremely helpful❤❤❤
Outstanding explanation ❤❤❤
Great to hear! Thanks for watching!
Good video! I just want to point out that if you are strictly using a double slit, the maximum amplitude of each maxima should decrease as you move away from the center. If you use an entire grating, what is shown would be basically accurate
Yeah, that’s a good point! I mean the gift of hindsight really comes out here. I could spout all kinds of stuff about Fourier transforms and optics now. But I’ll add that we’re obviously working on a small angle approximation here so the amplitude stays basically constant cause we’re saying the distance all the rays travelled is the same.
thank you so much!
thank you this works really well for a level
Great to hear thanks for watching
Thank you so much bro
My teacher has been explaining this to us in multiple lessons but i never got it but i immediately understood it by watching ur vid once
Thanks, that’s very kind! Glad it was helpful
class video lad
Nice video
thank you
Thank you
Thankyou
Thanks so muchhhh 😘
Hope that you can add subtiles in the upcoming videos because i'm not good at listening english.
Yeah will do, thanks for watching.
very good
Thanks for watching
Pattern does not oscilate from zero to some maaximum, its not a sinusoidal. Every peak getss lower and lower when you get further from center
In practice yes that’s true (explained by the single slit diffraction envelope). But the model for the double slit equation assumes two infinitely thin slits so there is no decay at the edges (again yes this isn’t super realistic but my phrasing was accurate).
Sorry then, i didnt realize you made that asumption. I just wanted to save some students confusion since its really tricky nowadays to find truly accurate information on the interenet. Thanks for being polite and accurate and for making this animations that help digest the material. 🙂🙂
Nice
Hi, could you also do a video on the double slit experiment with water? In a physics problem, we were given two slits that were 20 cm apart, so you can't apply the approximations made for light...
As a quick suggestion, as long as the viewing screen is much greater than 20cm (like a meter or couple of meters), then exactly the same approximations apply. Waves are a very general beast and all obey very far-reaching properties.
Let me know if the screen isn’t far away though
@@TheBrainFiller unfortunately, it isn't... We were supposed to describe the behaviour of an arbitrary point Q that is 16.0 cm away from the middle of the first slit and 28.0 cm away from the middle of the second slit.
I also asked ChatGPT, and it said that one should calculate the phase difference between the two waves arriving from S_1 and S_2, given lambda=6.0 cm and c=15.0 cm/s (and also amplitude=0.7cm)
If I do that, then I end up with a phase-shifted cosine-function that describes the displacement of the point Q as a function of time. I don't know if this is correct, but I hope it is.
I was looking for formulas that don't use the small angle approximation for sines and tangent, because we were then also supposed to calculate this: If the frequency of the wave is gradually cranked up, then the point Q will remain basically stationary at some unknown frequency, and this is a recurring phenomenon. They then want us to calculate the very first frequency where this is the case. Obviously, the point Q being stationary is caused by destructive interference from the waves coming from S_1 and S_2, and in order for that to happen, the phase difference between the two must be an uneven integer of pi. But, how the heck do I then go about calculating the frequency? ChatGPT said that the phase difference is somehow directly proportional to the wavelength, so an increase in the wavelength corresponds to an increase in the phase shift, somehow. Now, I don't know if this is actually correct. Let's assume that it is. Then, do I also assume that the speed of the wave stays constant? Since I could crank up the frequency either by decreasing the wavelength or by increasing the speed of the wave...
I understand what is going on physically, but I am a little bit lost as to how to actually go about calculating this.
Thank you for you reply, in any case.
Oh yeah if I’ve understood the question properly then chat gpt is about right. Find the phase difference between the two waves at the point based off the path difference and solve that way.
nice
why is one more appropriate for young's double slit whilst the other is for diffraction gratings?
That’s a fair question because people often call the n*lambda=d*sin(theta) equation the diffraction grating equation and then the other one is just used to find fringe spacing. However, I’m going to have to disagree with the premise of the question. Both formulas are equally appropriate for double slit and a diffraction grating (it just depends on what the question is asking you to find). Really the double slit is just a special case of the diffraction grating.
Hope that helps, feel free to ask for clarification
God