External Ventricular Drainage (EVD) and ICP Monitoring
Vložit
- čas přidán 22. 05. 2021
- The cranial vault contains brain tissue, blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). After closure of a child’s sutures, the cranial vault is similar to a rigid box. As the volume of the three components within the skull (brain matter, blood and CSF) must remain equal, an increase in one component must be accompanied by a decrease in another component. If there is not, an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) will occur.
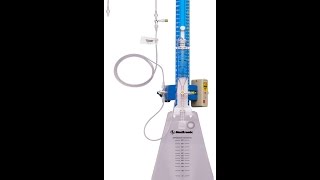
ICP can be monitored via a fibre optic monitor (Codman™ microsensor) which is placed on the surface of the brain or in the brain or an external ventricular drain (EVD) system which is a closed sterile system allowing drainage of CSF via a silastic catheter tip which rests in the ventricle.
The ventricular system produces CSF at approximately 20mL/hr (estimated at 0.35mL/min in children) by the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles. The CSF circulates around the brain and spinal cord and is then reabsorbed via the arachnoid villi.








Thank you so much for the detailed educational video. This is one of the best and clear video about EVD. Well done....
والله مبدع تحيه لك🌹❤
I needed a refresher and this was great!
Thanks a lot I have exam on this , it’s help a lot , new subscriber 💜
Just perfect! 👏
Such a great video!
Great video thank you
Good explain thank you
That was a great video!!!
thanks for sharing
This is really very helpful and one of the best videos about EVD and ICP monitoring. Thank you so much. You have gone so far with you great teaching skills :)
Thank you Islam,Miss you
Thabk you fornthis video
Thanks sir
انت عبقري
Awesome teaching
مافي عندو فيديوات عربي او الماني 😭😭😭
استمررررررررررررررررر
يا ريت الشرح يكون بلعربي
czcams.com/video/-fpdvHdwZ8Q/video.html
What is the name of scale used here?
you mean water scale?
احجي عربي فدوه
حياك الله اخي
موجود نسخة بالعربي