Premature rupture of membranes
Vložit
- čas přidán 27. 07. 2024
- This is a brief video on premature rupture of membranes, or the leakage of amniotic fluid before labor.
I created this presentation with Google Slides.
Images were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons
I created this video with the CZcams Video Editor.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Premature rupture
of membranes
10-week-old human fetus surrounded by amniotic fluid and fetal membranes
By drsuparna www.flickr.com/photos/74896762... - www.flickr.com/photos/74896762..., CC BY-SA 2.0, commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
Leakage of amniotic fluid before labor
Overview
Risk factors and causes
Diagnosis
Management
Chorio-
amnionitis
PROM = premature rupture of membranes
Amniotic sac rupture / fluid spillage more than one hour before onset of labor
Labor = regular contractions + cervical change
PPROM = preterm premature rupture of membranes
Amniotic sac rupture before 37 weeks
Prolonged rupture of membranes
Amniotic sac rupture for longer than 18 hours before delivery
“Gush of fluid†vs steady leakage of fluid
Note color and consistency of fluid
Thick vs watery
Clear, cloudy, meconium, blood-tinged
Overview
Overview
Risk factors and causes
Diagnosis
Management
Chorio-
amnionitis
Vaginal or cervical infections: UTIs, STIs, bacterial vaginosis
Smoking or drug use during pregnancy
PROM or preterm deliveries in previous pregnancies
Nutritional deficiencies; underweight mothers
Polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid)
Multiple gestation
Cervical insufficiency (short or prematurely dilated cervix)
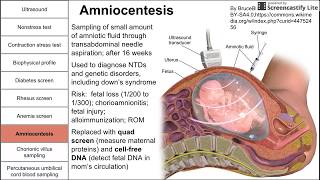
Invasive procedures (amniocentesis, cerclage, etc)
Pathophysiology:
Weak fetal membranes
Infections (sometimes subclinical)
Genetics
Risk factors and causes
Overview
Risk factors and causes
Diagnosis
Management
Chorio-
amnionitis
Three classic tests
Pooling: Collection of fluid in the vagina (posterior fornix)
Nitrazine: Neutral fluid turns nitrazine paper blue; vaginal fluid usually acidic. Amniotic fluid is mildly acidic → blue nitrazine paper
False positives: blood, semen, infections, antiseptics, lubricant
Ferning: Dry amniotic fluid on glass slide has crystallization pattern called arborization that resembles fern plant on light microscopy
Ultrasound can detect low levels of fluid (low residual fluid levels)
Other new tests detect chemicals or proteins in amniotic fluid
By Paul_012 - originally posted to Flickr as Positive fern test, CC BY-SA 2.0, commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
Management
Overview
Risk factors and causes
Diagnosis
Management
Chorio-
amnionitis
Previable
24 weeks
Watchful waiting; no tocolytics, steroids, MgSO4, or abx
Induction of labor to end pregnancy
Preterm
24-33 weeks
Tocolytics to prevent labor; steroids twice 24 hrs apart for lung maturity; MgSO4 as tocolytic while lungs mature; abx for GBS prevention
Amnioinfusion to replace lost fluid is controversial
Late preterm
34-36 weeks
Induce labor; abx for GBS prevention
Term
37 weeks
Induce labor; abx for GBS prevention
Definition: infection of chorion, amnion, and/or amniotic fluid surrounding fetus
Diagnosis:
Signs and symptoms: fever, rupture of membranes, leakage of fluid, uterine tenderness, elevated maternal heart rate ( 100 bpm), elevated fetal heart rate (160 bpm)
Fever: exclude maternal URI and UTI
Labs: increased white count ( 15,000 cells/mm³)
Treat with ampicillin, gentamicin, and clindamycin
Induce delivery
Covers gram negatives and anaerobes
Afebrile for 24 hours
Chorioamnionitis
Overview
Risk factors and causes
Diagnosis
Management
Chorio-
amnionitis
By Nephron - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...








Thanks🌹🙏
You are teaching very well....
FM resident starting my 4-week OB/GYN rotation in the AM--great overview, thank you so much!
That was a beautiful lecture, thank you so much
appreciate that man, GOOD content!!
This lecture was awesome thank you ❤️❤️
Thank you ❤
Great video
Thanks
thank you so much , very clear
Thank you very much
Thanks
thank you so much!
Thanks 🙏
💓💓💓💓💓💓Amazing
Crystal clear😃
cool dude
❤
Hallo, I just had pprom at 23 weeks with little leaking couple of days before a real gush on the day of induced labour.
I had been diagnosed with candidosis before and also actually contracted Covid-19 on 16 week of gestation.
All of the doctors said I had this situation due to Covid infection, is it possible?
Were you and your baby safe ?
@@lolalolatolala I was, but not the baby
@@AnnaVasylioglo my heartfelt condolences to you..